In her book Teacher Leadership That Strengthens Professional Practice, Charlotte Danielson defines teacher leadership as “that set of skills demonstrated by teachers who continue to teach students but also have an influence that extends beyond their own classroom to others within their own school and elsewhere.” Today, we are pleased to announce that the following individuals chose Fund for Teachers as their “elsewhere,” becoming our newest Educator Advisory Council members. After a thorough application and interview process by the Council’s seven founding members, these Fellows commit to a two-year term and help inform our organization’s work supporting and elevating the learning of teachers and their students. We are grateful to the following teachers for their commitment to their peers and our programming.
Hyam Elsaharty
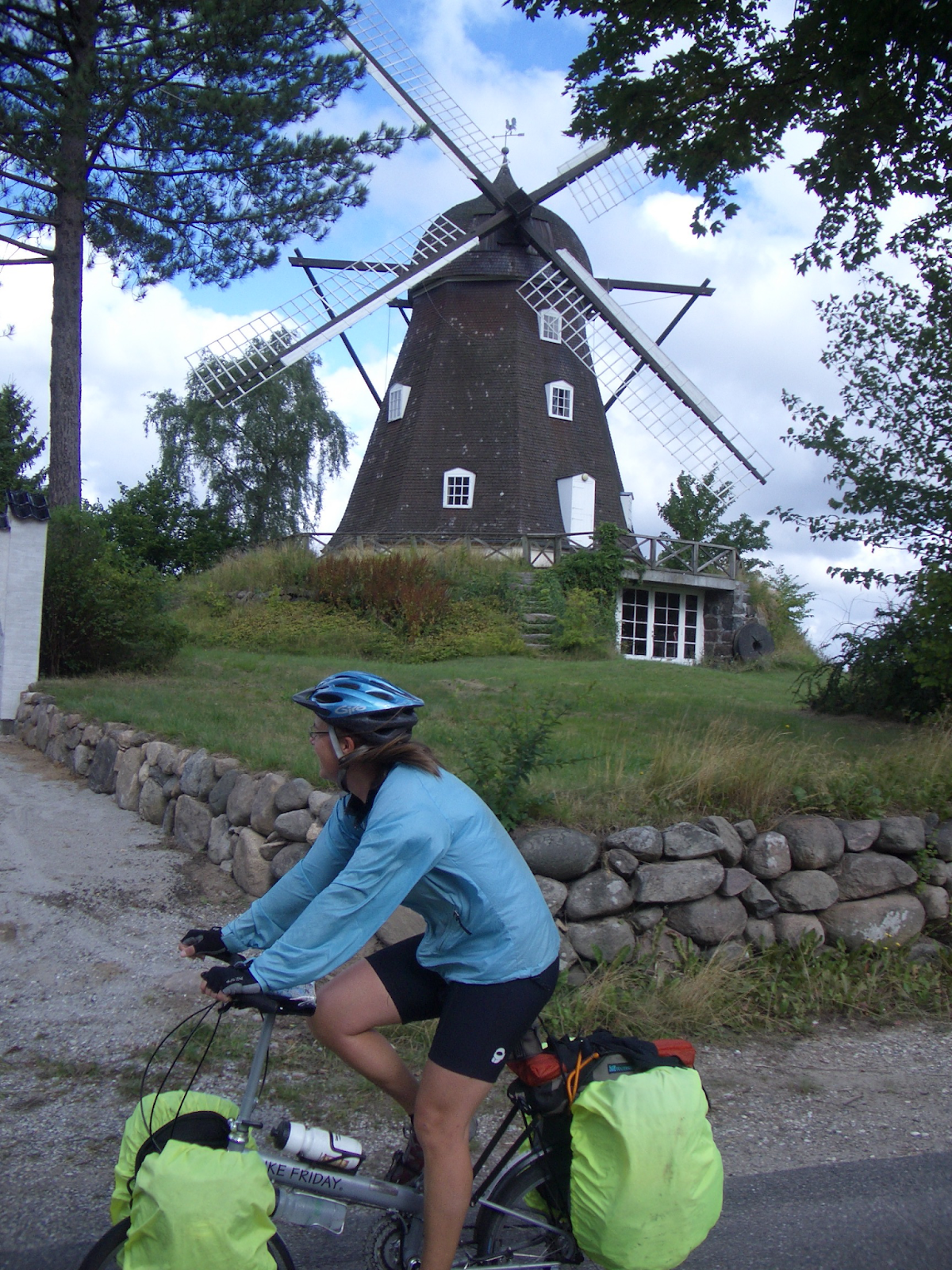
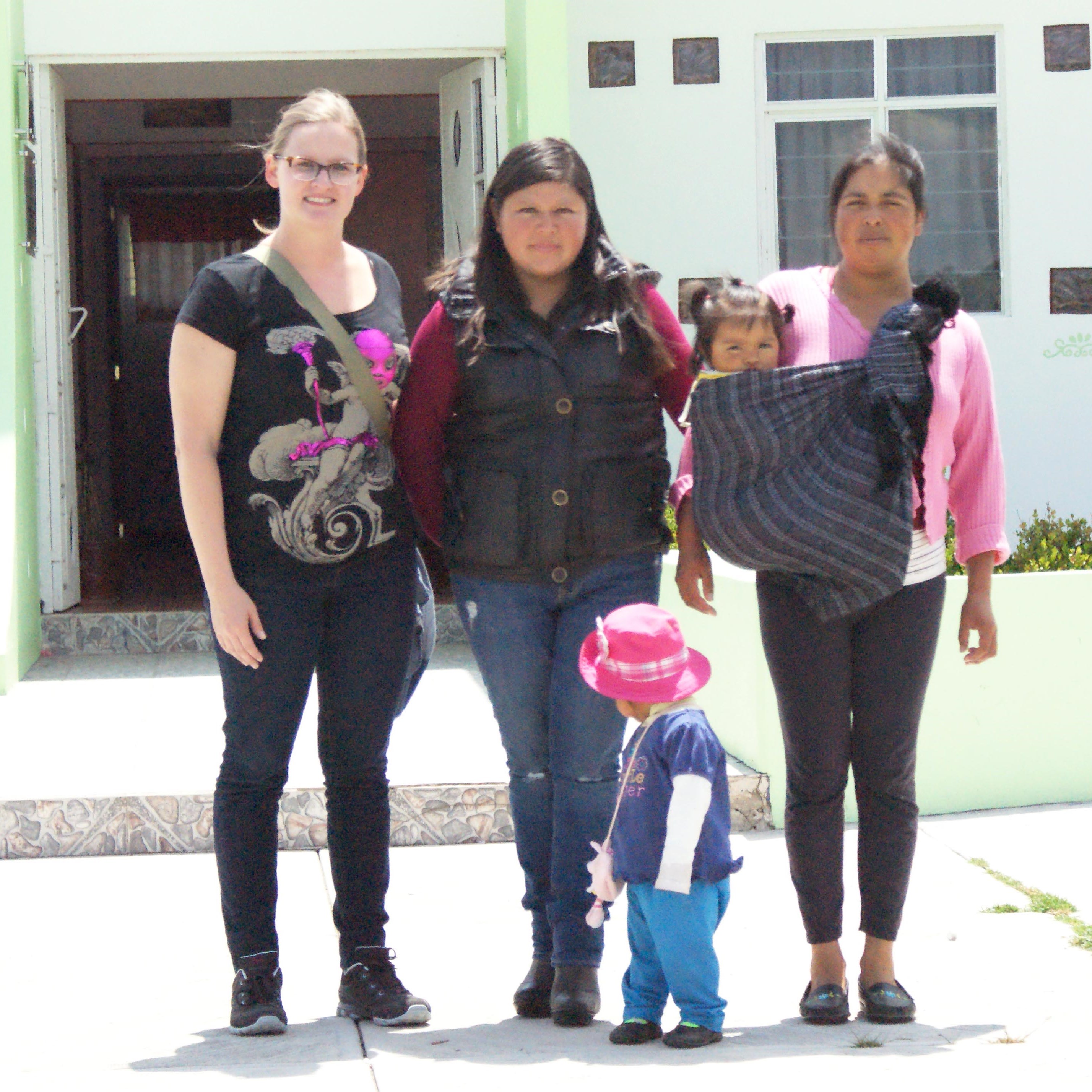
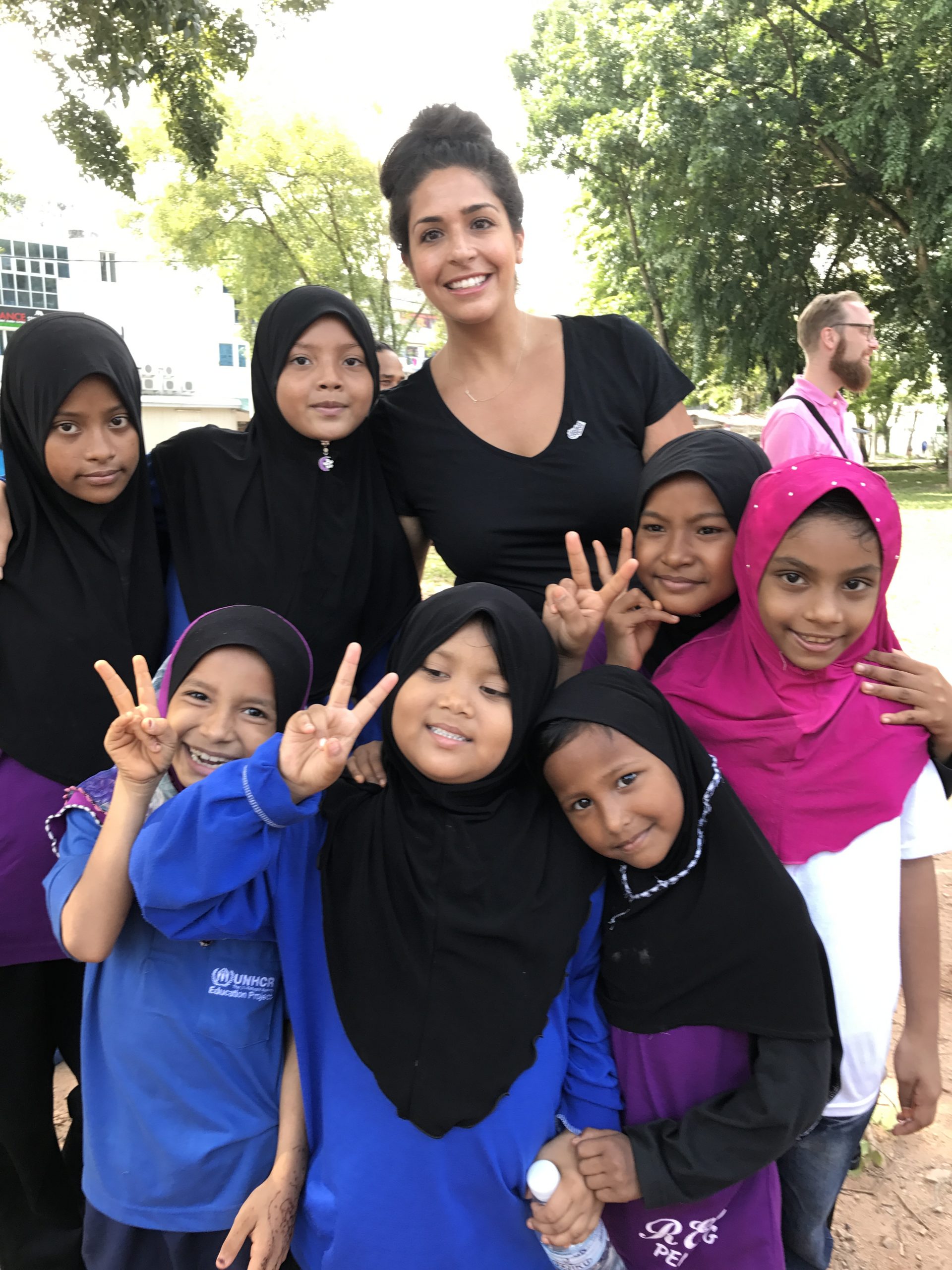 Prior to joining Seattle Public Schools as its District Social Emotional Learning Consulting Teacher, Hyam taught math and special education at Stephen T. Mather High School in Chicago, IL. In 2017, she and a colleague used a Fund for Teachers grant to investigate programs within refugee and public schools in Malaysia (pictured). Afterwards, the duo expanded existing advisory curriculum to meet the specific social and emotional needs of Malaysian and refugee students. In addition to her FFT fellowship, Hyam is also the recipient of the P. Buckly Moss grant and was named Chicago Public School’s SEL Teacher of the Year in 2019.
Prior to joining Seattle Public Schools as its District Social Emotional Learning Consulting Teacher, Hyam taught math and special education at Stephen T. Mather High School in Chicago, IL. In 2017, she and a colleague used a Fund for Teachers grant to investigate programs within refugee and public schools in Malaysia (pictured). Afterwards, the duo expanded existing advisory curriculum to meet the specific social and emotional needs of Malaysian and refugee students. In addition to her FFT fellowship, Hyam is also the recipient of the P. Buckly Moss grant and was named Chicago Public School’s SEL Teacher of the Year in 2019.
“Becoming an FFT Fellow was the impetus which began my life shift personally and professionally,” said Hyam. “As a woman of color who works in SEL where I get to help folks develop a sense and pride in their identity, self-advocate, and practice empathy, I am deeply committed and connected to the EAC’s objectives. In fact, without FFT I do not believe I would be secure in my own identity.”
Read more about Hyam’s fellowship here and her thoughts on social emotional learning in this Chalkbeat Chicago article.
Marco Cenabre
 Marco teaches high school literature at New Haven, CT, in the district where he was born, raised and from which he graduated. In 2019, he used his FFT grant to attend the Bard College Institute for Writing and Thinking in Annandale, NY, and afterwards award-winning author Debra Moffit’s “Gaining Creative Self Confidence Writing” retreat in Lake Annency, France, to implement intentional strategies in reflection and storytelling.
Marco teaches high school literature at New Haven, CT, in the district where he was born, raised and from which he graduated. In 2019, he used his FFT grant to attend the Bard College Institute for Writing and Thinking in Annandale, NY, and afterwards award-winning author Debra Moffit’s “Gaining Creative Self Confidence Writing” retreat in Lake Annency, France, to implement intentional strategies in reflection and storytelling.
“I believe in teacher-to-teacher collaboration, and leadership,” said Marco on why he chose to join the EAC. “One of the largest issues in teacher development is the fact that administrators, representatives of organizations, and others far removed from the classroom are the ones constructing the ‘solutions’ and offering them to teachers. It is through teacher innovation, reflection and a wide range of perspective that will spark what’s necessary in order for change to be truly enacted. Being a part of the EAC, and collaborating with others, will be an opportunity to offer solutions leading to widespread change.”
In addition to leading Fund for Teachers’ Social Justice Innovation Circle, Marco teaches a graduate course on reflective practice to first year teachers throughout the state, is a member of the Anti-Racist Teaching & Learning Collective and is a Teach for America alumni. Read more about Marco’s fellowship here.
Marin Leroy
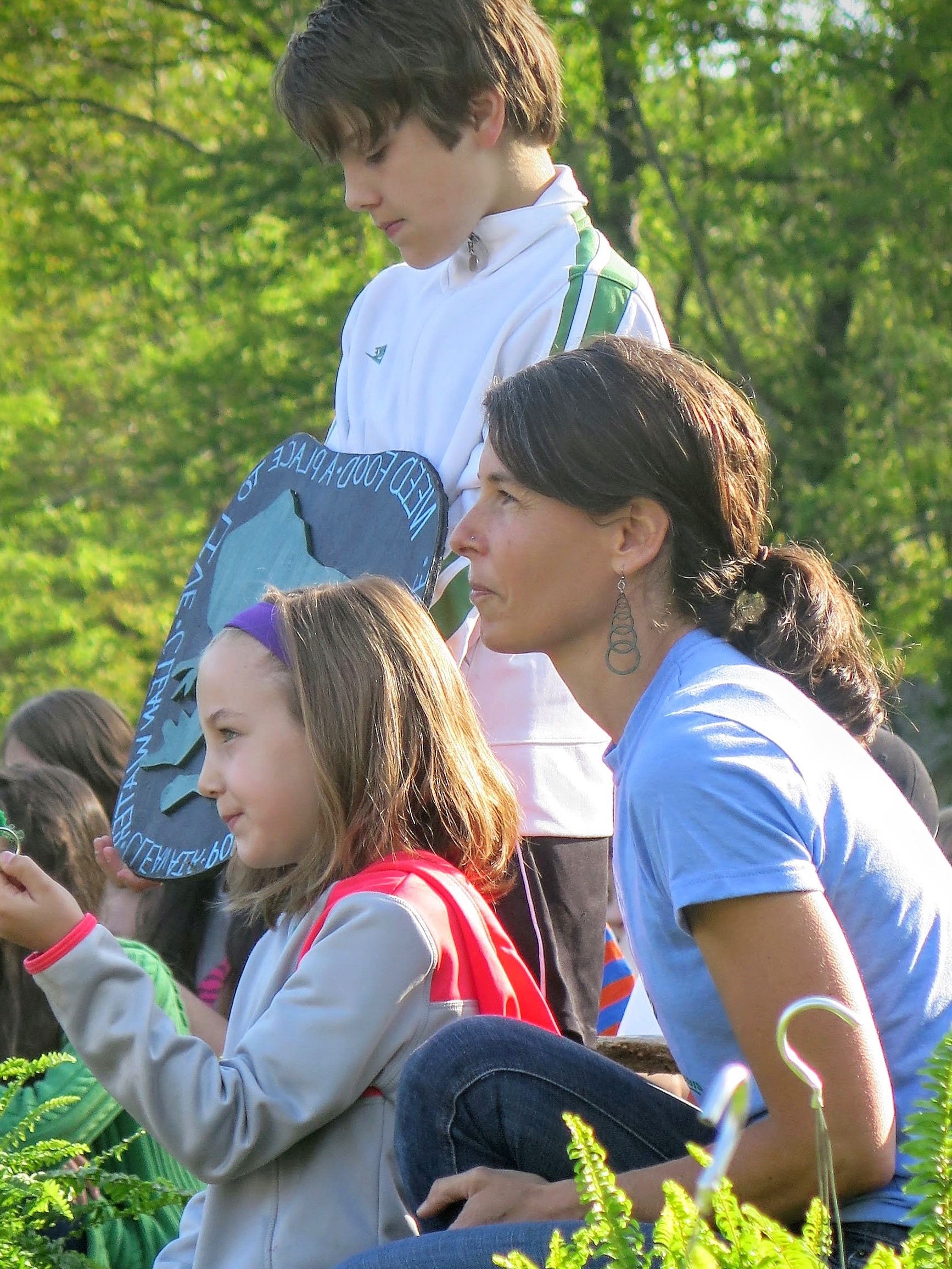 Marin teaches at Evergreen Community Charter School in Asheville, NC, where she coordinates for environmental education programs. In 2015, she used her grant to attend the week-long Edible Schoolyard Academy in Berkeley, CA, with subsequent mentoring at a K-8 Life Lab garden in Santa Cruz, CA. She returned to curate a team of educators from her broader community to support local edible education and school yard garden projects.
Marin teaches at Evergreen Community Charter School in Asheville, NC, where she coordinates for environmental education programs. In 2015, she used her grant to attend the week-long Edible Schoolyard Academy in Berkeley, CA, with subsequent mentoring at a K-8 Life Lab garden in Santa Cruz, CA. She returned to curate a team of educators from her broader community to support local edible education and school yard garden projects.
“My opinion is that most teacher certification programs give teachers a foundation, a starting place, but that FFT provides ways for educators to cultivate our own passions, which makes our teaching and facilitation of subject more highly engaging for students,” said Marin. “The more inspired we are as educators, the more we can spark our kids’ imagination and love for learning. As part of the EAC I will immerse myself in a community of professionals working to shift toward this academic paradigm through teacher engagement and inspiration.”
Read more about Marin’s community impact here.
Rao Olayeye
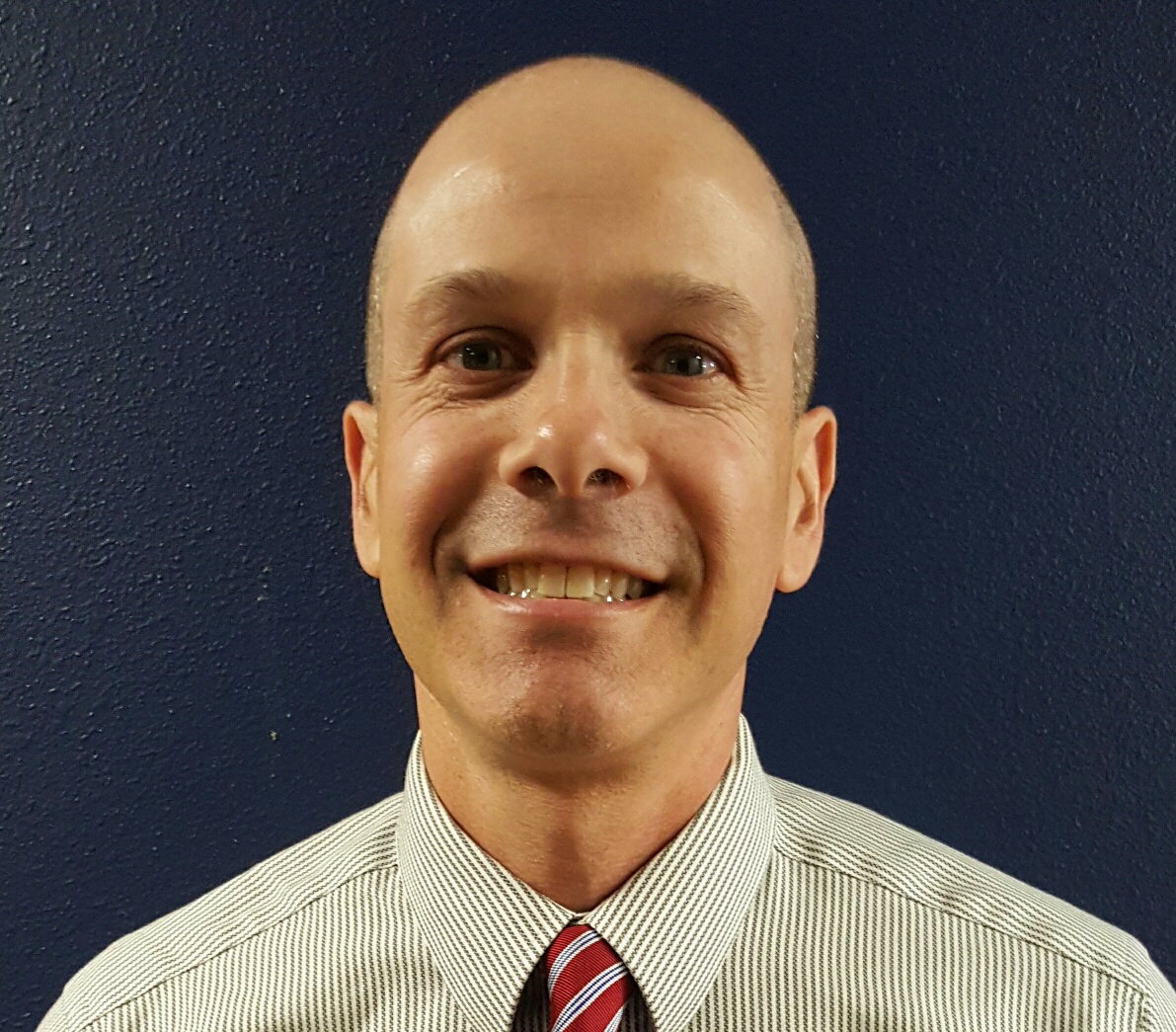
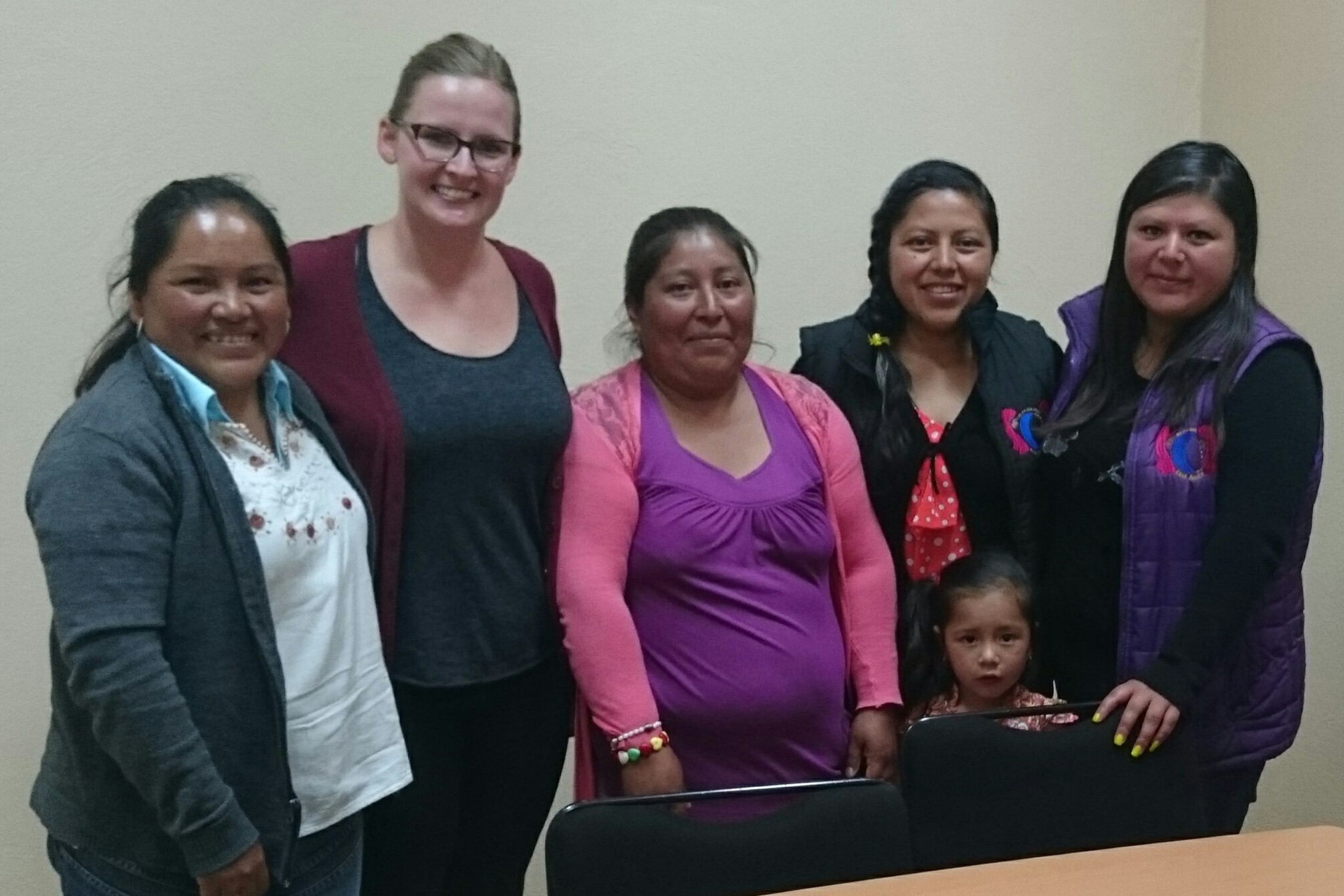
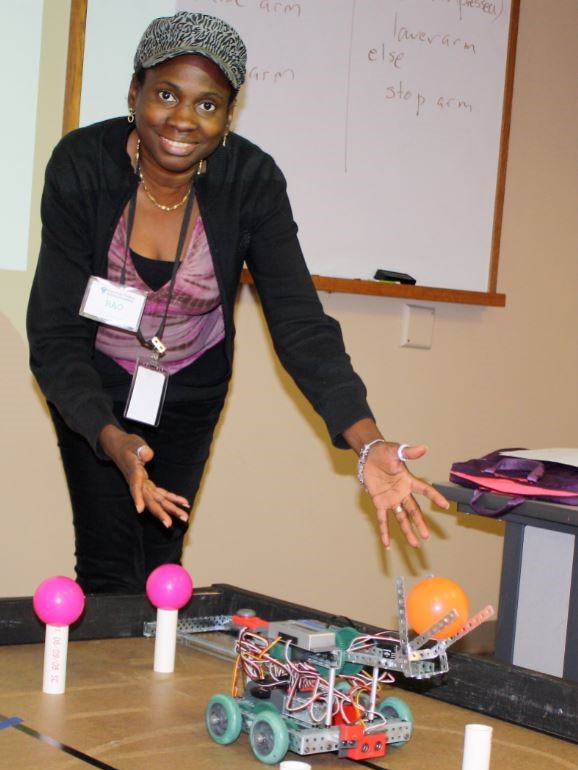 Rao recently returned from a teaching assignment in Bahrain, where she was the information technology specialist. Prior to that, she taught at the Atlanta International School, where she founded its middle school robotics program and developed the high school program into a competitive team. Her expertise in robotics began in 2012, when she used an FFT grant to attend a Robotics Education Global Conference in Oahu, HI, and enroll in Carnegie Mellon’s National Robotic Engineering Center in Pittsburgh, PA (pictured).
Rao recently returned from a teaching assignment in Bahrain, where she was the information technology specialist. Prior to that, she taught at the Atlanta International School, where she founded its middle school robotics program and developed the high school program into a competitive team. Her expertise in robotics began in 2012, when she used an FFT grant to attend a Robotics Education Global Conference in Oahu, HI, and enroll in Carnegie Mellon’s National Robotic Engineering Center in Pittsburgh, PA (pictured).
“There are not many women in educational leadership and I want to see a shift in that area,” said Rao on why she applied for an EAC position. “My masters and doctorate degrees, combined with years of experience teaching locally and internationally, are empowering me to be the change I want to see in the world and look forward to bringing that passion and commitment to the EAC to benefit a wider community.”
Victoria Thomson
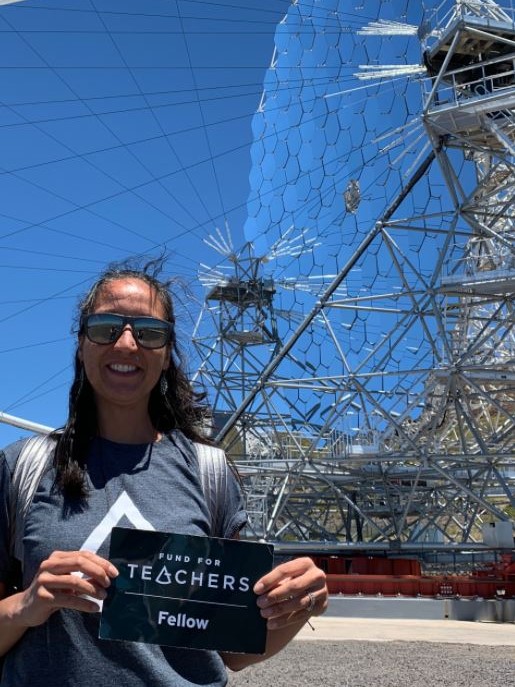 Victoria teaches Integrated Science and astronomy in East Lyme, CT, after a career as a scientist/entomologist. In 2019, she used her FFT grant to participate in a summer teacher training course sponsored by the Galileo Teacher Training Program in the Canary Islands, home to some of the most technologically-advanced telescopes in the Northern Hemisphere (pictured).
Victoria teaches Integrated Science and astronomy in East Lyme, CT, after a career as a scientist/entomologist. In 2019, she used her FFT grant to participate in a summer teacher training course sponsored by the Galileo Teacher Training Program in the Canary Islands, home to some of the most technologically-advanced telescopes in the Northern Hemisphere (pictured).
When asked why she wanted to join the EAC, Victoria responded, “I am the first generation to go to college in my family and ended up thriving at an Ivy League School. I wanted to give back to students and inspire them, which is why I became a teacher. As an adult, I see teachers get stuck by the barriers placed on them in the classroom. I see and hear teachers feel like victims of a system. I want to be a part of a group that inspires teachers to find other teachers to be rise up together and be brave, to do what is best for our children, our future leaders.”
Read more about Victoria’s fellowship here.















 [minti_divider style=”3″ icon=”” margin=”20px 0px 20px 0px”]
[minti_divider style=”3″ icon=”” margin=”20px 0px 20px 0px”]
























 Neha Singhal is a high school teacher in Maryland who has taught students in several courses: IB Anthropology, Government, U.S. History, Latin American Studies, and College/Career Prep. She has also taught various courses in Asian American Studies at the University of Maryland, College Park and University of Maryland, Baltimore County. Prior to becoming an educator, Neha worked with
Neha Singhal is a high school teacher in Maryland who has taught students in several courses: IB Anthropology, Government, U.S. History, Latin American Studies, and College/Career Prep. She has also taught various courses in Asian American Studies at the University of Maryland, College Park and University of Maryland, Baltimore County. Prior to becoming an educator, Neha worked with 





